Pentest - Stealing Chrome Cookies
Stealing Chrome Cookies
source: mango.pdf.zone
Using Chrome’s remote debugging protocol to steal cookies. github - defaultnamehere
- requires rce on victim’s machine
Defense
Infostealers, Token Theft, Azure
https://www.varonis.com/blog/cookie-bite
Context
Most infostealers don’t use the stolen data directly. Instead, they operate within a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) model, where different actors play specialized roles. Those roles can include:
- Infostealer operators developing and distributing malware to infect as many victims as possible
- Tracers (affiliates) spreading the malware through phishing tactics, malicious ads, or software cracks
- Darknet marketplaces serving as a hub where cybercriminals sell stolen cookies, credentials, and browser fingerprints in bulk
- Buyers (from initial access brokers and ransomware groups) purchasing these credentials to gain unauthorized access to cloud services, corporate VPNs, and sensitive platforms
Session hijacking
Adversary in the Middle (AITM)
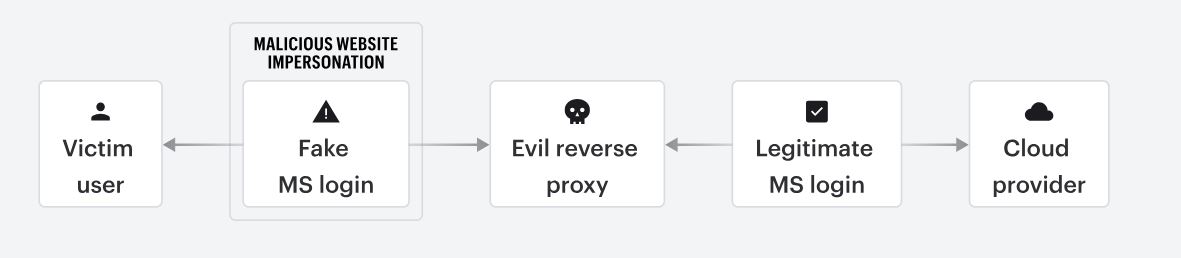
AITM phishing attacks go beyond traditional credential theft by intercepting authentication tokens and session cookies in real-time. Attackers use reverse proxy tools (e.g., Evilginx, Modlishka, Muraena) to sit between the victim and the legitimate authentication service (e.g., Microsoft 365, Google).
When the victim logs in, the proxy captures credentials, MFA tokens, and session cookies, allowing the attacker to bypass MFA and hijack the session without needing the user’s password again. This technique is widely used to compromise cloud accounts and bypass modern authentication defenses.