Windows Kernel
The Windows Kernel
There are two parts of the running operating system: the kernel and the user-mode applications. The kernel makes the security decisions that determine what a user can do on the system. Most of the applications you use on a Windows machine run in user mode.
The Windows NTOS kernel executive
The kernel provides all the OS’s privileged functionality, as well as interfaces through which user applications can communicate with the hardware. The kernel is split into multiple subsystems:
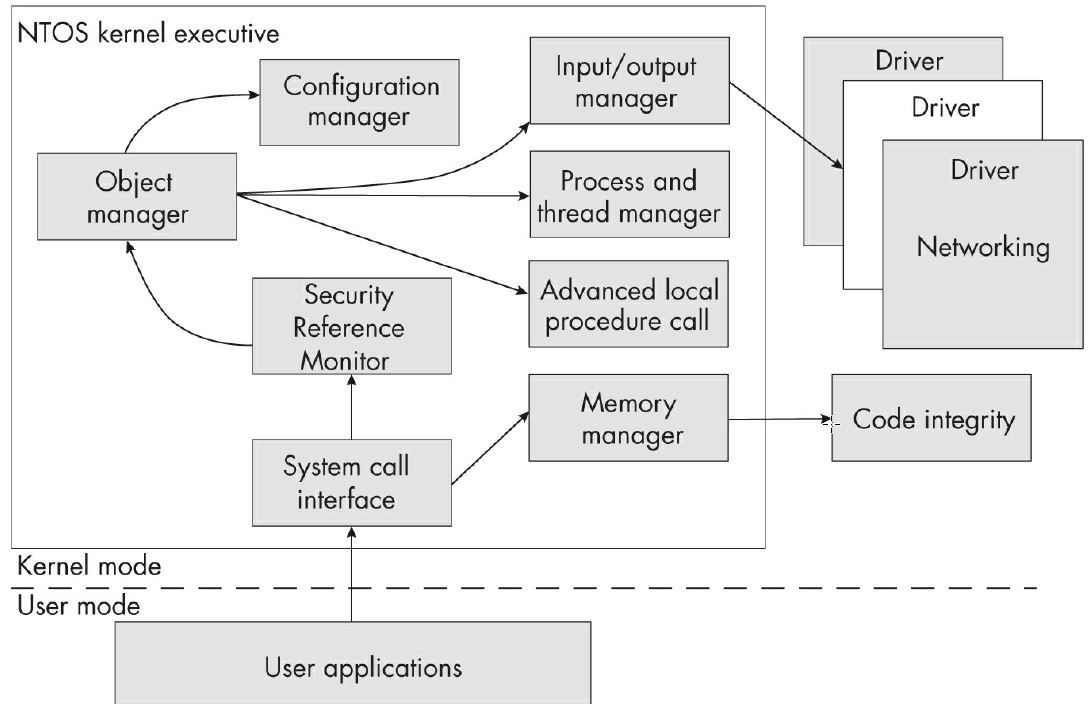
Each subsystem exposes APIs for the other subsystems to call.
- API Prefix-to-Subsystem Mapping
| Prefix | Subsystem | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Nt/Zw | System call interface | NtOpenFile / ZwOpenFile |
| Se | Security Reference Monitor | SeAccessCheck |
| Ob | Object manager | ObReferenceObjectByHandle |
| Ps | Process and thread manager | PsGetCurrentProcess |
| Cm | Configuration manager | CmRegisterCallback |
| Mm | Memory manager | MmMapIoSpace |
| Io | Input/output manager | IoCreateFile |
| Ci | Code integrity | CiValidateFileObject |