Windows Kernel - Security Reference Monitor
Windows Kernel - Security Reference Monitor
The Security Reference Monitor (SRM) implements the security mechanisms that restrict which users can access different resources.
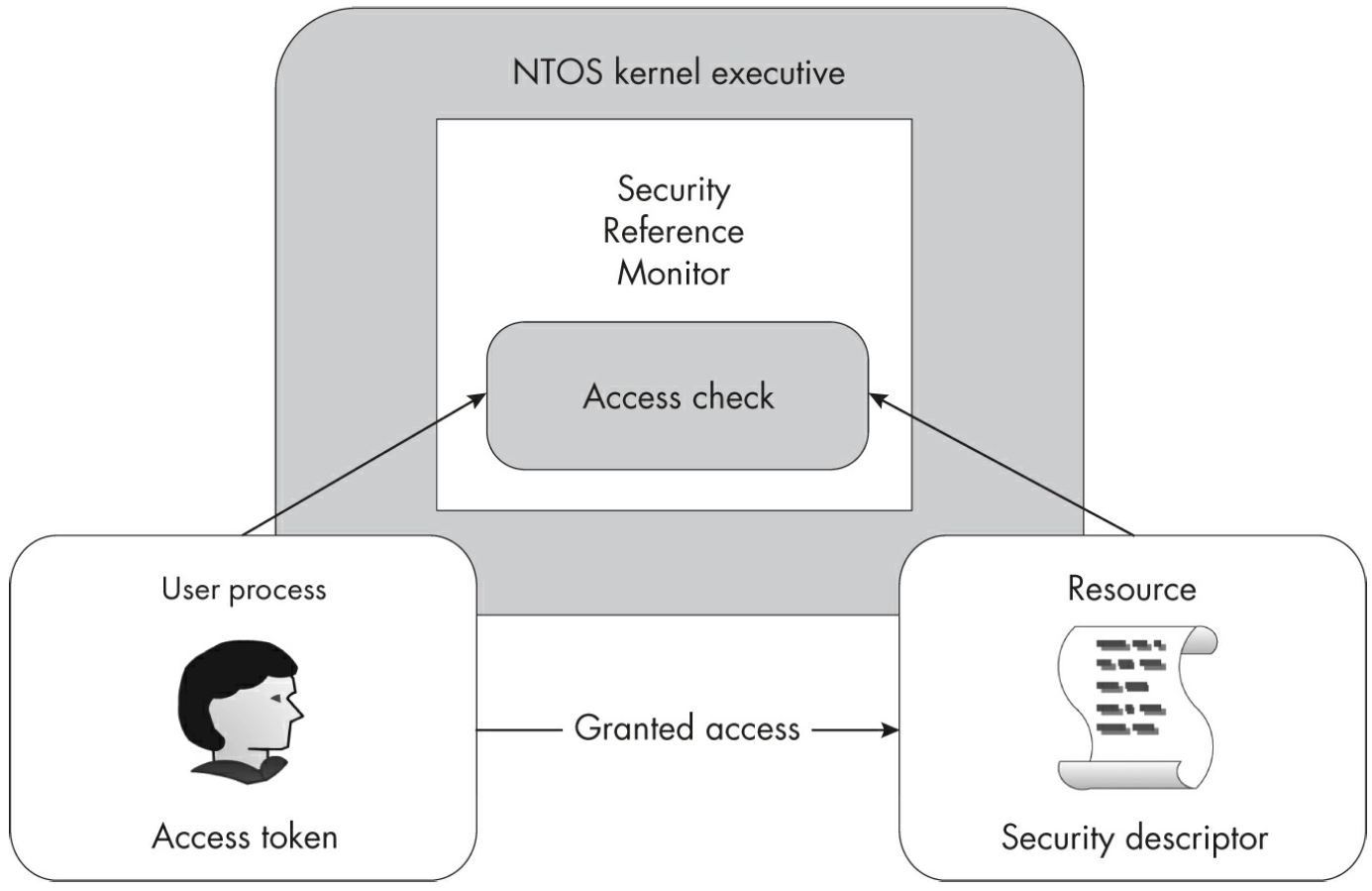
Every process running on the system is assigned an access token when it’s created. This access token is managed by the SRM and defines the identity of the user associated with that process. The SRM can then perform an operation called an access check. This operation queries a resource’s security descriptor, compares it to the process’s access token, and either calculates the level of granted access or indicates that access is denied to the caller.
The SRM is also responsible for generating audit events whenever a user accesses a resource. Auditing is disabled by default due to the volume of events it can produce, so an administrator must enable it first. These audit events can be used to identify malicious behavior on a system as well as to diagnose security misconfigurations.
The SRM expects users and groups to be represented as binary structures called security identifiers (SIDs). The task of name–SID conversion is handled by the Local Security Authority Subsystem (LSASS), which runs inside a privileged process independent from any logged-in users. Microsoft defines the Security Descriptor Definition Language (SDDL) format to represent a SID as a string.