XOR #cryptography
XOR
Basics
Exclusive or – ‘XOR’ – is a Boolean binary operator that is true when either the first input or the second input, but not both, are true.
XOR is a ‘programmable inverter’: one input bit decides whether to invert the other input bit or to just pass it through unchanged. ‘Inverting’ bits is also called ‘flipping’ bits.
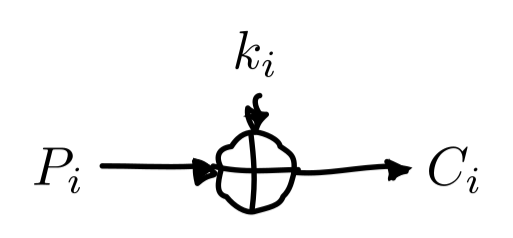
Inputs and outputs above are named as if XOR were being used as an encryption operation, with plaintext bit, key bit, ciphertext bit. The operator is written as \(\bigoplus\) or caret ^.
Truth table
- 0 ^ 0 = 0
- 0 ^ 1 = 1
- 1 ^ 0 = 1
- 1 ^ 1 = 0
Examples
- 5 ^ 3 = (101) ^ (011) = (110) = 6
- 10 ^ 2 = (1010) ^ (0010) = (1000) = 8
Properties
\[ \frac{1}{2} \int f(x) dx \nabla^2\phi(x) \]